Selective protection technology for low-voltage distribution systems and requirements for circuit breakers at all levels
2021-05-09
Selective protection means that the action characteristics of two or more protection devices cooperate with each other. When a short circuit, grounding or other overcurrent occurs within a specified range, the device that specifies the action within this range acts to remove Failure, and the device outside this range does not work. That is, when an overcurrent fault occurs at a certain point in the low-voltage power distribution system, the electrical equipment of the power distribution performs a selective breaking action according to a predetermined action sequence, and the over-level trip is absolutely not allowed. The important significance of selective protection is that when the low-voltage distribution system has a short-circuit fault, grounding and other overcurrent phenomena, the protection device in the power distribution system must be able to reliably remove the fault and ensure the minimum power outage range.
1. System selective protection technologyIn the area of short-circuit protection, it is very difficult to realize the protective tripping of the circuit Breaker in the low-voltage distribution system, which requires the following methods to cooperate with each other.
1.1 Current selectivity
When a short-circuit fault occurs in the low-voltage power distribution system, the difference in the magnitude of the short-circuit current measured by the upper and lower circuit breakers may be caused according to the difference in the line impedance of the system, and the current is selectively protected. This protection is achieved by the different action values of the trip units in the circuit breakers of adjacent stages. This method can be applied to the protection of Class A molded case circuit breakers, miniature circuit breakers and residual action current circuit breakers. According to the relevant standards, it is generally required that the minimum instantaneous current of the circuit breaker 1 is not less than 1.4 times the minimum instantaneous current of the circuit breaker 2.
1.2 time selectivity
When the short-circuit current is large, the selective protection can be realized according to the different operating time of the upper and lower circuit breakers. The disconnection work process of the circuit breaker is as follows: after the short circuit fault occurs, the trip unit is automatically tripped, the contacts of the circuit breaker are disconnected under the action of the operating mechanism, and the arc generated during the process is extinguished by the arc extinguishing device, and the circuit breaker is broken. The work is done. The time from the start of the short circuit to the time before the release of the trip unit is about to be released is called the trip time; the time from the occurrence of the short circuit until the completion of the full partial break is called the full break time. In order to ensure time selectivity, the circuit breaker must be satisfied: in the amperage characteristic curve, the trip time of the main circuit breaker is greater than the full breaking time of the branch circuit breaker.
For Class A circuit breakers, the tripping curves of the upper and lower adjacent two-stage circuit breakers do not intersect or overlap in the overload zone, but in the instantaneous zone, the two curves may cross or even coincide. Therefore, in order to achieve time selectivity, the upper circuit breaker should adopt a Class B circuit breaker with current withstand capability and short circuit delay.
1.3 virtual time selectivity
When the lower-level wiring adopts the current-limiting type circuit breaker, the short-circuit current of the upper-level incoming line is related to the current-limiting coefficient. The smaller the current-limiting coefficient, the smaller the short-circuit current will be, and the longer the operation time of the line will be. Therefore, the current-trip characteristic curve is an inverse time characteristic, which enhances the selective protection characteristics of the wiring and the incoming line.
1.4 logical selectivity
Logical selectivity, also known as regioselective interlocking. The realization of logic selective protection is based on the premise that the lower level circuit breakers have communication functions and intelligent functions. The logic-selective working procedure is as follows: 1) After the lower-level circuit breaker fails and detects the fault, the upper-level circuit breaker sends a signal to prevent it from tripping; 2) the upper-level circuit breaker receives the non-tripping command and executes the command. 3) The lower-level circuit breaker trips to remove the faulty power supply; 4) The upper-level circuit breaker remains closed, or tripped if the lower-level circuit breaker does not trip within the set time. Figure 1 below is an example.
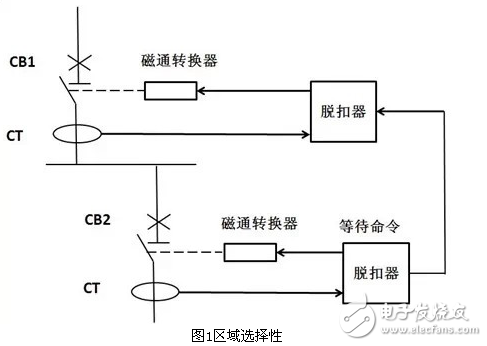
The working principle is as follows: 1) When the outgoing line of the circuit breaker CB2 fails, the CB2 circuit breaker is disconnected, and the fault is removed. 2) When the circuit breaker CB2 fails, the trip unit of circuit breaker CB2 automatically sends a signal to the trip unit of the upper circuit breaker CB1, so that the current trip time of CB1 is changed to the delay time, if the delay time is exceeded. The circuit breaker CB2 still does not trip, and the circuit breaker CB1 has a tripping failure. 3) If the fault current after the fault of the circuit breaker CB2 is far greater than its bearing capacity, the circuit breaker CB1 will immediately trip and remove the fault regardless of whether the signal of CB2 is received or not.
1.5 energy selectivity
Energy selectivity refers to the technology of selective protection based on the short-circuit energy of the tripping capacity of the tripping device based on the upper and lower circuit breakers with current limiting capability. When a fault occurs and the upper and lower circuit breakers detect a large current, the lower circuit breaker has a fast current limiting speed, so that the short circuit energy is lower than the energy of the tripping action of the upper circuit breaker, so that the upper circuit breaker cannot operate. It can be seen from the energy curve of the upper and lower circuit breaker that the condition for achieving energy selectivity is that the short circuit energy curve of the lower circuit breaker is lower than that of the upper circuit breaker.
2. Low-voltage power distribution system requirements for circuit breakers at all levelsThe selective protection technology of the low-voltage power distribution system has the following requirements for the circuit breakers of all levels.
2.1 incoming line cabinet
The main switch of the incoming line cabinet adopts frame circuit breaker, which should meet the following requirements: intelligent controller, which can realize online fault monitoring, action value setting, communication and other control functions; rated short-circuit limit segmentation capability, rated short-circuit operation breaking capacity and The rated short-time withstand current is equal, and the currents of 0.2s, 0.5s, and 1s are listed respectively; the controller's ability to resist electromagnetic interference should be strong; the short-circuit delay time is 0.2-0.5s.
2.2 power distribution cabinet
The power distribution cabinet mainly adopts molded case circuit breaker, which should meet the following requirements: current limiting type, the current limiting capacity of small capacity circuit breaker should be below 6-10kA; with short circuit delay of 0.2-0.4s, it is best to set The value can be adjusted by three-stage protection; it has communication function, which is conducive to the realization of regional selective interlock; the circuit breaker with electronic trip unit requires high anti-electromagnetic interference capability; it has a certain rated short-time withstand current.
2.3 terminal
The main components of the distribution system terminal are miniature circuit breakers, which should meet the following requirements: use current-limiting products; have a certain rated short-time withstand current, such as 0.2s, 10-20kA; adjustable protection setting; leakage The current and voltage values of the protector or the leakage circuit breaker are adjustable.
2.4 current shortcomings
Current circuit breakers are not able to meet all the requirements for protection selectivity of low voltage distribution systems. For example, a small-current molded case circuit breaker has an electronic trip unit, but it is limited by size and has no short-circuit delay function; most molded case circuit breakers and miniature circuit breakers have no rated short-time withstand current. The requirements of intelligent circuit breakers are too high. Although split group control measures can be adopted, how to deal with the tripping of fault circuits in priority is still to be studied. At present, the tripping mechanism of molded case circuit breakers has little energy selectivity. Wait. These issues require further research and resolution.
3. Implementation points and implementation of selective protection design3.1 Determination of the form of selective protection
Selective protection technologies mainly include both fully selective protection and partial selective protection. Fully selective protection means that the fault occurs between the upper and lower circuit breakers and is within the protection range of the lower circuit breaker. When the fault current occurs between the overload setting value and the three-phase short-circuit current value, it is tripped by the lower-level circuit breaker. Fault, the upper circuit breaker remains inoperative, ensuring the selectivity of protection. Partially selective protection means that when the fault current is greater than a predetermined value, the characteristic curve of the upper and lower circuit breakers has an intersection point, and all the selectivity cannot be guaranteed. At this time, below a certain lower fault current value, the upper and lower stages are disconnected. The device is selectively matched.
When configuring a circuit breaker in a low-voltage power distribution system, the ideal situation is that full selectivity can be obtained between the upper and lower stages; if full selective protection is not possible, it can only be followed by a partial selection. Usually, we adjust the line structure and path in the power distribution system according to the requirements, and calculate the short-circuit current. If the calculated value is lower than the selective limit current value, the system is selective; if the selective limit current value is exceeded , the upper circuit breaker is malfunctioned and the protection selectivity is lost.
If the power supply load is not allowed to be powered off, efforts should be made to ensure protection selectivity. The circuit breaker must be reconfigured and the calculated short-circuit fault current is less than the selective limit current. If the load is not affected, it is partially selected. .
3.2 Carefully design low-voltage distribution system to distribute load reasonably
In the design of low-voltage power distribution system, the load should be reasonably distributed. In order to meet the requirements of the rated current ratio of the protection device, the ratio of the load of the upper and lower stages should be increased as much as possible. The selectivity requirement is more easily satisfied when the ratio of the upper and lower stage loads is larger.
Whether it is circuit breaker protection or fuse protection, in order to achieve the selective protection requirements, the rated current ratio of the upper and lower protectors must be greater than a certain set value.
Therefore, when designing the selective protection of low-voltage distribution systems, the upper and lower loads should be properly adjusted according to the standard requirements, and the natural distribution load must not be allowed. At the same time, “natural” selective protection should be adopted as much as possible to provide selective protection. Provide convenience to meet protective requirements. Otherwise, other selective protection methods will be adopted, which will result in neither economical nor troublesome.
3.3 Circuit breaker short circuit short delay selective protection precautions
The most common way to achieve selective protection of circuit breaker protection is short-circuit short-delay protection. Pay attention to the following points:
1) Minimize the delay time
The delay time of the circuit breaker should be shortened as much as possible while satisfying the selectivity. Because the short-circuit current experienced by the circuit breaker is large during the delay time, this increases the manufacturing requirements of the circuit breaker and increases the cost. At the same time, the delay time is too long, which will cause the system voltage to fluctuate greatly, which is not conducive to the stable operation of the system. Therefore, the short-circuit delay time should be carefully selected, and the delay time should not be increased arbitrarily.
2) Reasonably determine the number of distribution stages
When the short-circuit short-delay selection type circuit breaker is used in the low-voltage power distribution system, the delay time can be changed by changing the number of power distribution stages, the number of power distribution stages is reduced, and the delay time of the upper-level power distribution is also reduced accordingly. In a specific power distribution system, the number of power distribution stages of the power distribution system should be reasonably determined based on actual conditions and various factors.
3) Proper use of "natural" selective methods
In the actual low-voltage distribution system, there are few selective methods that use short-circuit short-delay, and all “natural” selective methods rarely appear. Low-voltage distribution systems mostly use a hybrid, selective approach, and this mutual combination is also reasonable. In principle, the “natural” selective method is used as much as possible, and in the local system, especially the intermediate and terminal power distribution parts, the “natural” selective mode is adopted.
4) Three-stage protection of the circuit breaker
When the circuit breaker adopts three-stage protection of over-current, short-circuit short-delay and instantaneous quick-action protection, the difference of short-circuit current between the upper and lower stages is small, and when the short-circuit fault occurs in the lower stage, the upper and lower circuit breakers will trip, not Guarantee the selectivity of protection. In this case, the instantaneous quick-action protection of the superior must be released, and only the short-circuit delay is used for protection.
If the long line fails, the instantaneous quick-action protection action will reduce the protection range, but it should also be put into the instantaneous quick-action protection as much as possible, and cut off the short-circuit fault within the protection range as soon as possible to avoid damage to the line and electrical devices. Reduce the economic loss caused by short circuit faults.
4 ConclusionRealizing the protection selectivity of the low-voltage power distribution system can effectively ensure the reliability of the system power supply. The current choice of protective technology needs to be further improved and improved. It is believed that with the continuous development of technology, the low-voltage power distribution system will be improved and the reliability of power supply will be further improved.
KNB1-63 Mini Circuit breakers, also named as the air switch which have a short for arc extinguishing device. It is a switch role, and also is a automatic protection of low-voltage electrical distribution. Its role is equivalent to the combination of switch. Fuse. thermal relay and other electrical components. It mainly used for short circuit and overload protection. Generally, According to the poles, mini Circuit breaker can be divided into 1P , 1P+N , 2P, 3P and 4P.
KNB1-63 Miniature Circuit Breaker, Electronics Miniature Circuits Breaker, Automatic Miniature Circuit Breaker, Mini Circuit Breaker
Solar Energy Product Co., Ltd. http://www.korlen-electric.com









